ACHI BIZ is your personalized premium service provider when it comes to seeking business management assistance in Singapore.
ACHI BIZ provides with our experts for the taxation services such as for GST, individual Income Tax and Corporate Income Tax for all types of Firms and Entities in Singapore.
Goods and Services Tax or GST is a broad-based consumption tax levied on the import of goods (collected by Singapore Customs), as well as nearly all supplies of goods and services in Singapore. In other countries, GST is known as the Value-Added Tax or VAT.
GST exemptions apply to the provision of most financial services, the sale and lease of residential properties, and the importation and local supply of investment precious metals. Goods that are exported and international services are zero-rated.
Increase of GST rate (What is the change of GST rate in Singapore?)
In Budget 2022, the Minister for Finance announced that the GST rate will be increased from:
(i) 7% to 8% with effect from 1 Jan 2023; and
(ii) 8% to 9% with effect from 1 Jan 2024.
Effect on GST-registered businesses – what you need to do
The rate change affects any GST-registered business that sells or purchases goods or services that are subject to the standard rate of GST.
First rate change from 7% to 8%
For any standard-rated supplies of goods or services that you make on or after 1 Jan 2023, you must charge GST at 8%. For instance, if you issue an invoice and receive payments for your supply on or after 1 Jan 2023, you must account for GST at 8%.
If you are a GST-registered business that is subject to reverse charge (“RC business”), you must account for GST at 8% on the services you procure from overseas suppliers (“imported services”) on or after 1 Jan 2023.
However, there are special transitional rules for supplies that span the change of rate. This may affect the GST rate chargeable on the supply.
You may refer to the e-Tax Guide 2023 GST Rate Change: A Guide for GST-registered Businesses (PDF, 663KB) for more information on rate change.
Preparing for the GST rate change
You are strongly encouraged to prepare early for a smooth transition to the new GST rate. For example, you may need to modify your point-of-sale, invoicing, accounting and other systems, as well as your price displays to reflect the new rate.
Please refer to the Checklist for GST rate change preparation on the changes that may be required to your systems and business processes to apply the new rate.
Current Taxable and Non-Taxable Goods and Services
The table below lists the categories and types of taxable and non-taxable supplies.
|
Taxable Supplies |
Non-Taxable Supplies |
|
Standard-Rated Supplies
(7% GST)
|
Zero-Rated Supplies
(0% GST)
|
Exempt Supplies
(GST is not applicable)
|
Out-of-Scope Supplies
(GST is not applicable)
|
Goods
|
Most local sales fall under this category.
E.g. sale of TV set in a Singapore retail shop |
Export of goods
E.g. sale of laptop to overseas customer where the laptop is shipped to an overseas address |
Sale and rental of unfurnished residential property
Importation and local supply of investment precious metals |
Sale where goods are delivered from overseas to another place overseas
Private transactions
See Out-of-scope supplies for more information. |
Services
|
Most local provision of services fall under this category.E.g. provision of spa services to a customer in Singapore |
Services that are classified as international services
E.g. air ticket from Singapore to Thailand (international transportation service) |
Financial services
E.g. issue of a debt security |
Businesses Required to Register for GST
As a business, you must register for GST when your taxable turnover exceeds $1million.
If your business does not exceed $1 million in taxable turnover, you may still choose to voluntarily register for GST after careful consideration.
Please refer to IRAS webpage at
www.iras.gov.sg for more information on whether you need to register for GST.
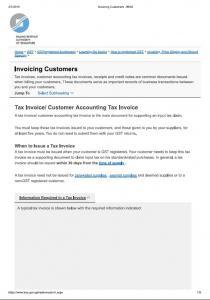
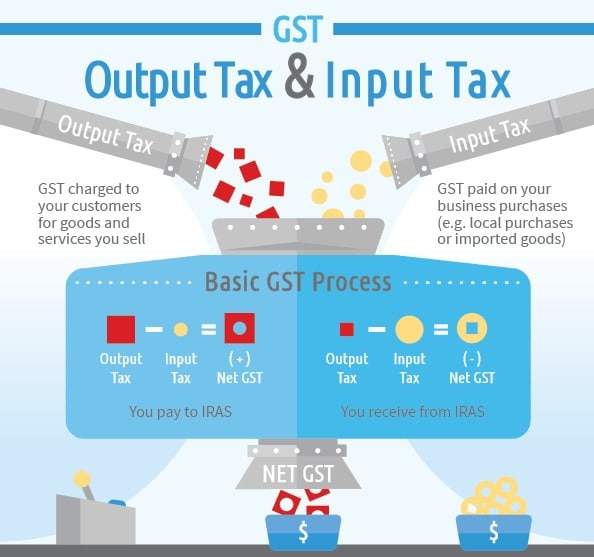
Charging and Collecting GST
Once you have registered for GST, you must charge GST on your supplies at the prevailing rate with the exception of relevant supplies that are subject to customer accounting. This GST that is charged and collected is known as
output tax. Output tax must be paid to IRAS.
The GST that you incur on business purchases and expenses (including import of goods) is known as
input tax. If your business satisfies the conditions for claiming input tax, you can claim the input tax on your business purchases and expenses.
This input tax credit mechanism ensures that only the value added is taxed at each stage of a supply chain.
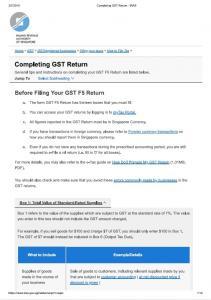
Paying Output Tax and Claiming Input Tax Credits
As a GST-registered business:
- You must submit your GST return to IRAS one month after the end of each prescribed accounting period. This is usually done on a quarterly basis.
- You should report both your output tax and input tax in your GST return.
- The difference between output tax and input tax is the net GST payable to IRAS or refunded by IRAS.
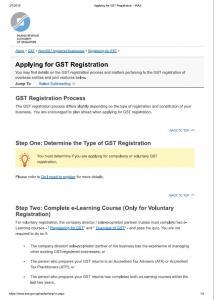
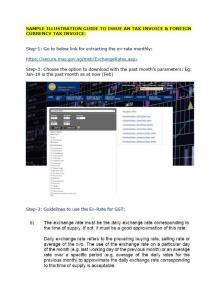
Refer to the below links for GST e-Tax Guides from registration till cancellation with Sample Illustration Guide for more information (source from IRAS):
|
|
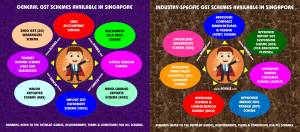
Cash Accounting Scheme
- The Cash Accounting Scheme is designed to alleviate the cash flow of small businesses. Under the scheme, businesses only have to account for output tax when payment is received.
|
Discounted Sale Price Scheme
- Under the Discounted Sale Price Scheme, you can charge GST on 50% of the selling price when you sell a second-hand / used vehicle. You do not need to seek prior approval from IRAS to use the scheme.
|
Gross Margin Scheme
- Second-Hand dealers who purchased goods free of GST may use the Gross Margin Scheme to charge and account for GST.
|
Hand-Carried Exports Scheme (HCES)
- Effective 1 April 2009, the Hand-Carried Exports Scheme (HCES) is applicable if you wish to zero-rate your supplies to overseas customers for goods hand-carried out of Singapore via Changi International Airport.
|
Import GST Deferment Scheme (IGDS)
- Under IGDS, approved GST-registered businesses pay GST on imports payments when their monthly GST returns are due instead of at the point of importation.
|
Major Exporter Scheme (MES)
- Under MES, GST on non-dutiable goods is suspended at the point of import and also when the goods are removed from Zero GST warehouses.
|
Tourist Refund Scheme (TRS) for Businesses
- GST-registered businesses may provide GST refunds to tourists as an independent retailer or by engaging the services of a Central Refund Agency. In either case, they need to do so under the electronic Tourist Refund Scheme (eTRS).
|
Zero GST (ZG) Warehouse Scheme
- The Zero GST (ZG) Warehouse Scheme is administered by Singapore Customs. Under this scheme, import GST on non-dutiable overseas goods is suspended when the goods are moved into a ZG warehouse. GST is payable only when the imported goods leave the warehouse and enter the local market.
|
|
|
Approved Contract Manufacturer and Trader (ACMT) Scheme
- Contract manufacturers and traders under this scheme are relieved of the need to account for GST on value added activities supplied to non-GST registered overseas customers.
|
Approved Import GST Suspension Scheme (AISS) (For Aerospace Players)
- Under AISS, GST-registered businesses in the aerospace industry enjoy added import GST suspension benefits for qualifying aircraft parts.
|
Approved Marine Customer Scheme (AMCS)
- Under AMCS, GST-registered businesses enjoy zero-rating on purchases or rental of goods and repair or maintenance services on ship parts or components under qualifying conditions.
|
Approved Marine Fuel Trader (MFT) Scheme
- Under MFT Scheme, approved businesses need not pay GST when making local purchases of approved marine fuel oil from any GST-registered suppliers.
|
Approved Refiner and Consolidator Scheme (ARCS)
- Under this scheme, Approved Refiners and Approved Consolidators enjoy certain benefits including GST suspension on qualifying imports and additional input tax benefits.
|
Approved Third Party Logistics (3PL) Company Scheme
- Under this scheme, approved logistics companies that provide logistics management services to overseas clients do not need to pay import GST or charge GST on the supplies of their overseas clients’ goods under certain circumstances.
|
Specialised Warehouse Scheme (SWS)
- Under this scheme, qualifying services performed on qualifying goods in Approved Specialised Warehouses and the lease/ tenancy/ licence of storage space in these warehouses can be zero-rated to overseas persons.
|
Rectification / Amendment of errors in GST Return in Singapore:
You may request for a GST F7 for the affected prescribed accounting period at myTax Portal to disclose the errors made. Please complete the GST F7 with the revised figures (including all adjustments) for all boxes as it will supercede the previous GST return (GST F5 or a previous GST F7) submitted for the accounting period.
However, depending on the nature and amount of the error made, you may be allowed to adjust for the error in your GST F5 for the next accounting period.
Correcting Errors in Your GST Return:
If you have made errors in your submitted GST F5/ F7/ F8 forms, you should file GST F7 to correct the errors.
Administrative Concession by IRAS for Correcting Errors:
As an administrative concession, you may choose to adjust for the errors made in your next GST F5 if you meet both of these criteria:
- The Net GST amount in error (i.e. output tax error – input tax error) for all the affected prescribed accounting periods is not more than $1,500; and
- The total non-GST amounts in error for (each of) the affected accounting period(s) is not more than 5% of the total value of supplies declared in the submitted GST return (i.e. Box 4). In the case where there was no supply made in the affected accounting period, the 5% rule applies to the total value of the taxable purchases (i.e. Box 5).
However, the administrative concession does not apply to:
- Errors that affect Boxes 9 to 12 of your past GST F5.
- Errors made in your last return, GST F8.
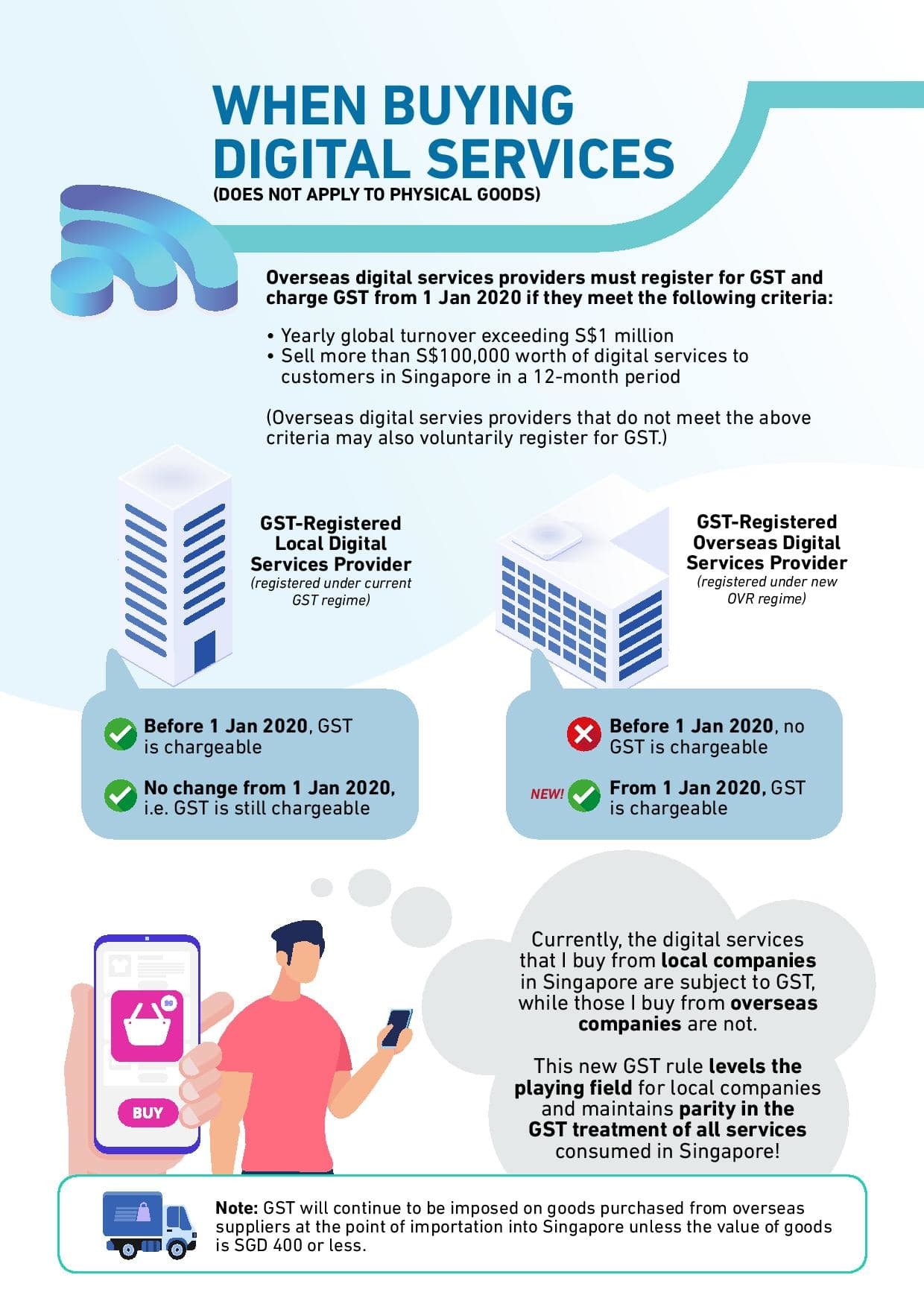
GST payable on overseas digital services from 1 Jan 2020
From 1 Jan 2020, GST is chargeable on digital services bought from GST-registered overseas service providers.
Here’s what you need to know as a digital consumer:
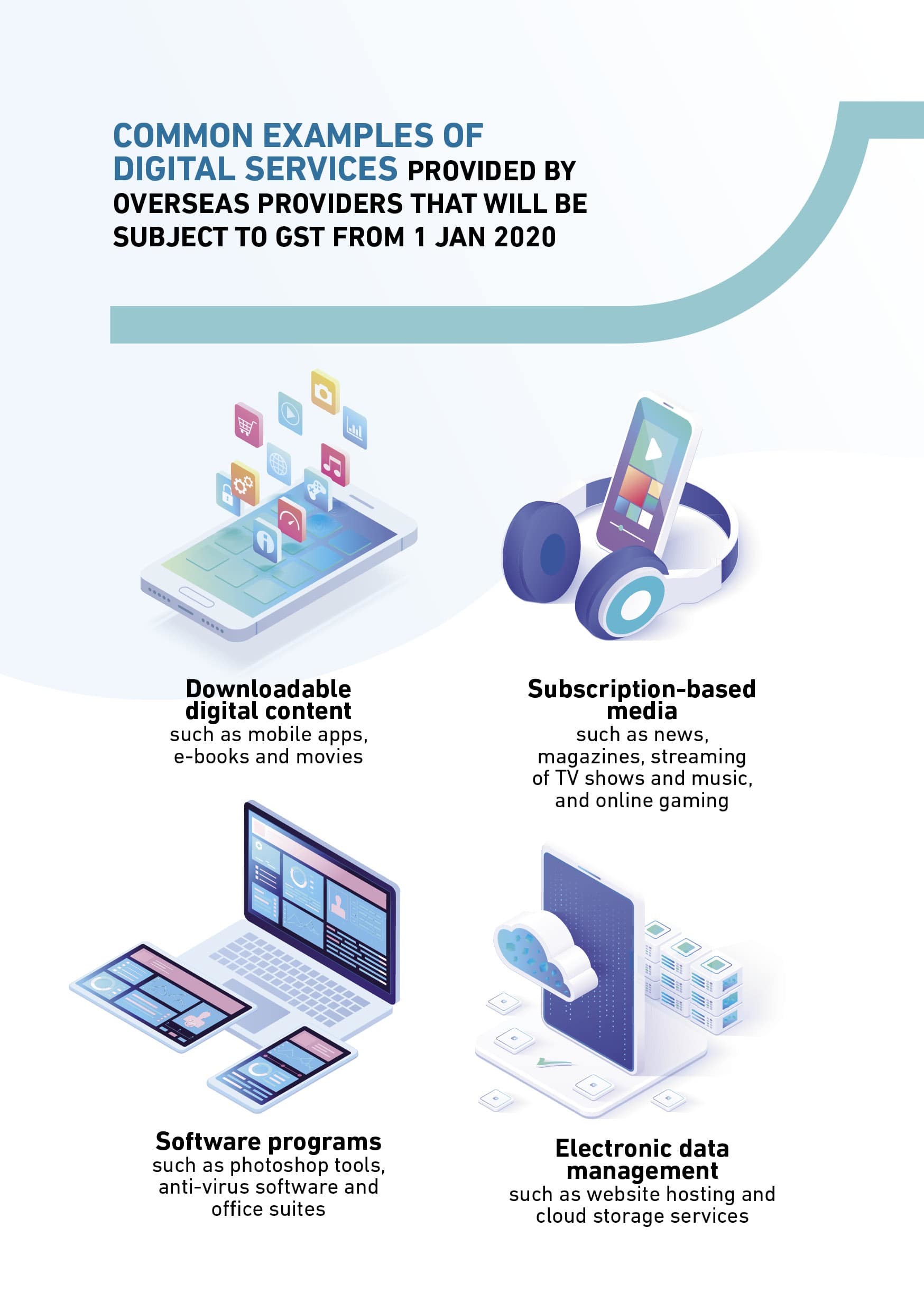
- From 1 Jan 2020, GST is chargeable on movie and music streaming services, as well as other digital services bought from GST-registered overseas providers.
- Digital services provided by overseas providers include downloadable digital content, subscription-based media, software programmes, web hosting services, etc.
- Note: Not all overseas service providers can charge GST. Be vigilant!
- Check whether an overseas provider is registered at https://go.gov.sg/gstlistingsearch
Under the OVR regime, overseas digital service providers with a yearly global turnover of more than S$1 million that sell more than S$100,000 worth of digital services to customers in Singapore in a 12-month period are required to register for GST and charge GST.
Examples of digital services purchased from overseas service providers include:
Meanwhile, there will be no changes in the GST treatment for online purchases of goods: GST remains payable on all goods imported into Singapore, with the exception of goods valued S$400 and below imported via air or post.
What consumers need to do
As overseas digital service providers use information such as payment and billing information to determine if customers reside in Singapore, businesses and consumers are responsible for providing complete and accurate information to registered overseas digital service providers. It is a serious offence to provide incorrect or false information to overseas digital service providers to avoid paying GST on digital services.

- To maintain the integrity of your financial positions & reports
- Tired of too many absenteeism
- Availing even unpaid leave for frequently for holidaying
- Demanding regular increment
- If there is no increment then working with unhappiness & with no target
- Demanding Thirteenth month salary & bonus even while your business is on negative
- Hard to retain for long run
- Negative feedback about your management to the new employees or online
Please CONTACT us if you wish to know more about this service or many other services.
 GST In Singapore
GST In Singapore


 When you encounter with any of the following issues with your Book-Keeping &/or Accounting staff then we strongly suggest you to consider for outsourcing to ACHI as our costs are fixed basis per annum:
When you encounter with any of the following issues with your Book-Keeping &/or Accounting staff then we strongly suggest you to consider for outsourcing to ACHI as our costs are fixed basis per annum: 24/7/365
24/7/365